
The statement of retained earnings is one of four main financial statements, along with the balance sheet, income statement, and statement of cash flows. In that case, the company may choose not to issue it as a separate form, but simply add it to the balance sheet. It’s also sometimes called the statement of shareholders’ equity or the statement of owner’s equity, depending on the business structure. It is a temporary account used to summarize revenues and expenses before transferring the net income or net loss to the retained earnings account on the balance sheet. After closing, its balance is reflected in the retained earnings on the balance sheet.
Retained earnings at closing entry
Ultimately, the company’s management and board of directors decides how to use retained earnings. Retained earnings is the residual value of a company after its expenses have been paid and dividends issued to shareholders. Retained earnings represents the amount of value a company has “saved up” each https://www.bookstime.com/articles/how-to-calculate-overtime-pay year as unspent net income. Should the company decide to have expenses exceed revenue in a future year, the company can draw down retained earnings to cover the shortage. Retained earnings is calculated as the beginning balance ($5,000) plus net income (+$4,000) less dividends paid (-$2,000).

How to Calculate an Income Summary Account?
The resultant number may be either positive or negative, depending upon the net income or loss generated by the company over time. Alternatively, the company paying large dividends that exceed the other figures can also lead to the retained earnings going negative. Cash payment of dividends leads to cash outflow and is recorded in the books and accounts as net reductions. As the company loses ownership of its liquid assets in the form of cash dividends, it reduces the company’s asset value on the balance sheet, thereby impacting RE.
What is the retained earnings formula?
Retained earnings can be used to pay off existing outstanding debts or loans that your business owes. When it comes to investors, they are interested in earning maximum returns on their investments. Where they know that management has profitable investment opportunities and have faith in the management’s capabilities, they would want management to retain surplus profits for higher returns. In this article, you will learn about retained earnings, the retained earnings formula and calculation, how retained earnings can be used, and the limitations of retained earnings. Below is a short video explanation to help you understand the importance of retained earnings from an accounting perspective.
- When a company generates net income, it is typically recorded as a credit to the retained earnings account, increasing the balance.
- Implementing accounting software can help ensure that each journal entry you post keeps the formula and total debits and credits in balance.
- Yes, the income summary is a temporary account used to summarize revenues and expenses for a specific period before transferring the net income or net loss to the retained earnings account.
- This usually gives companies more options to fund expansions and other initiatives without relying on high-interest loans or other debt.
- As stated earlier, companies may pay out either cash or stock dividends.
- Retained earnings appear on the balance sheet under the shareholders’ equity section.
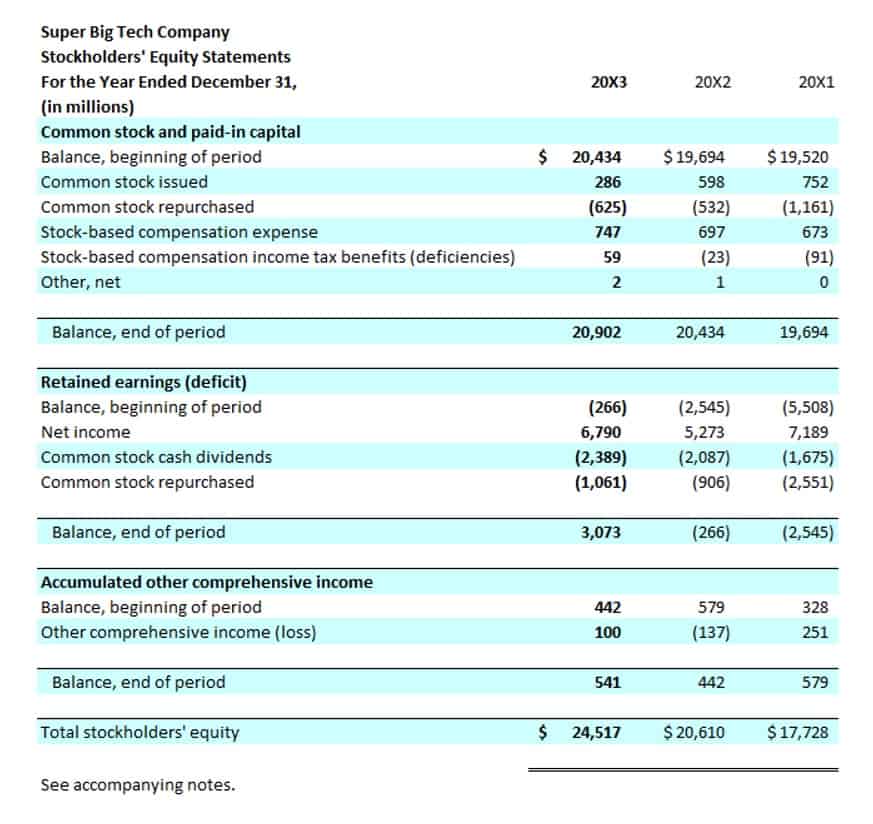
The owner’s equity and shareholders’ equity accounts are the common interest in your business, represented by common stock, additional paid-in capital, and retained earnings. The statement of retained earnings is a financial statement entirely devoted to calculating your retained earnings. Like the retained earnings formula, the statement of retained earnings lists beginning retained earnings, net income or loss, dividends paid, and the final retained earnings. It is useful to note that although the retained earnings account has a normal balance on the credit side, the company may have the debit balance of retained earnings instead. In this case, this debit balance of retained earnings will be presented as a negative in the balance sheet.
A separate formal statement—the statement of retained earnings—discloses such changes. Also, keep in mind that the equation you use to get shareholders’ equity is the same you use to get your working capital. It’s a measure retained earnings a debit or credit of the resources your small business has at its disposal to fund day-to-day operations. Retained are part of your total assets, though—so you’ll include them alongside your other liabilities if you use the equation above.

Retained earnings refer to the portion of a company’s net income or profits that it retains and reinvests in the business instead of paying out as dividends to shareholders. It’s an equity account in the balance sheet, and equity is the difference between assets (valuables) and liabilities (debts). Net income increases Retained Earnings, while net losses and dividends decrease Retained Earnings in any given year. Thus, the balance in Retained Earnings represents the corporation’s accumulated net income not distributed to stockholders. At the end of each accounting period, businesses close out their revenue and expense accounts, summarizing them into a temporary account known as the Income Summary Account. The net balance (revenue – expenses) of this account is then transferred to Retained Earnings through closing entries.
Additional Paid-In Capital
Many of these come in the form of understanding what each section of the document means and interpreting it. In many cases, the computer never even shows the income summary or has a record. To gain a better understanding of what these temporary accounts are, take a look at the following example. Both cash and revenue are increased, and revenue is increased with a credit.
- Thus, it is a liability of the company and it is credited as per the golden rules of accounting for personal accounts.
- The normal balance in a profitable corporation’s Retained Earnings account is a credit balance.
- Like the retained earnings formula, the statement of retained earnings lists beginning retained earnings, net income or loss, dividends paid, and the final retained earnings.
- For example, if the dividends a company distributed were actually greater than retained earnings balance, it could make sense to see a negative balance.
How to Calculate the Effect of a Stock Dividend on Retained Earnings?


